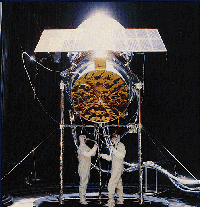
The Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) was a joint project of the
US, UK and the Netherlands. The IRAS mission perform an unbiased, sensitive
all sky survey at 12, 25, 60 and 100 microns. IRAS increased the number
of cataloged astronomical sources by about 70%, detecting about 350,000
infrared sources. IRAS discoveries included a disk of dust grains around
the star Vega, six new comets, and very strong infrared emission from interacting
galaxies as well as wisps of warm dust called infrared cirrus which could
be found in almost every direction of space. IRAS also revealed for the
first time the core of our galaxy, the Milky Way. The satellite design
and survey strategy were optimized for maximally reliable detection of
point sources. Pointed observations, known as Additional Observations or
AOs, were also done, interspersed with the survey
observations. Catalogs of Point Sources derived from these data are
available.
