|
Wind Scatterometer |
|
| Contents
Wind
Scatterometer
|
The Wind Scatterometer is part of the Active Microwave Instrument, (AMI) orbiting on the European Space Agency satellite ERS-2. It obtains information on wind speed and direction at the sea surface for incorporation into models, global statistics and climatological datasets. Wind scatterometers record the change in radar reflectivity or backscatter of the ocean due to the wind produced ripples on the surface. Accurate measurements of the radar backscatter from the ocean surface when illuminated by the radar signal with a narrow bandwidth is processed to derive information on ocean surface wind velocity. The amount of backscatter depends on two factors - the size of the surface ripples of the ocean, and their orientation compared to the direction of the radiation pulse transmitted by the scatterometer. The first is dependent on wind stress and hence wind speed at the surface, while the second is related to wind direction. Measurements by the ERS scatterometer may be used to derive both wind speed and direction. Because microwave wavelengths cna penetrate clouds and are not dependent on solar radiation, the measurements are not weather or time of day dependent. "The three antennae generate radar beams looking 45° forward, sideways, and 45° backwards with respect to the satellite's flight direction. These beams illuminate a 500 km wide swath as the satellite moves along its orbit. Three backscatter measurements of each grid point are obtained at different viewing angles and separated by a short time delay. These "triplets" are fed to a mathematical model which calculates surface wind speed and direction." http://earth.esa.int/rootcollection/eeo4.10075/scatt_design.html
The First and Second European Remote-Sensing Satellites (ERS-1 and ERS-2) were developed by the European Space Agency as a family of multi-disciplinary Earth Observation Satellites. They orbit the Earth in about 100 minutes and in 35 days cover nearly every corner of the globe at least once. ERS-1 launched in July 1991. ERS-2, the successor of ERS-1, was launched on 21 April 1995. ERS-1 was decommissioned in March of 2000.
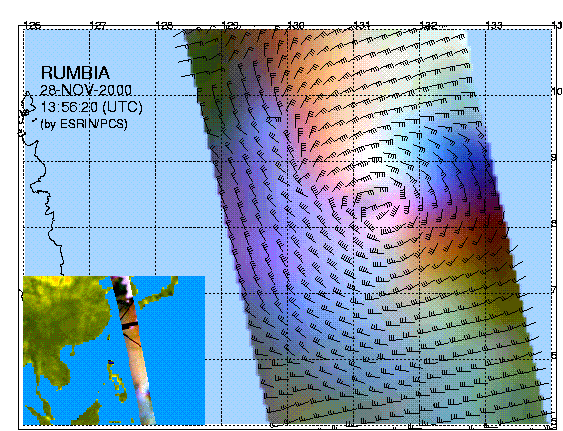
ERS-2, based SPOT satellite design Data products from the wind scatterometer are available from Earthnet Online (http://earth.esa.int/services). The 1/2 Wind Scatterometer Fast Delivery Product is generated with data from the Wind Scatterometer. This global product of 500 x 500 km frames gives wind speed and direction at nadir, plus the radar backscatter values for the three beams of the scatterometer. An example is below:
Data acquired on 28th November 2000 Resources European Space Agency site http://earth.esa.int/services/pg/- ESA products available |
|---|---|
|
Web Publications Dr. Young's Homepage Geography Department Salem State College
updated April 28, 2004 |
|