|
What
is NEXRAD?
 |
NEXRAD is an active remote
sensing system. |
.
 |
NEXRAD is an acronym for next
generation radar. |
 |
NEXRAD is also known as WSR88D
which stands for Weather Surveillance Radar 1988 Doppler. |
 |
NEXRAD is a system of Doppler
radar sites installed by the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric
Administration (NOAA). |
 |
NEXRAD's purpose is to track
precipitation and weather systems in the United States. |
 |
NEXRAD can also be used to
track other objects in the atmosphere such as smog, pollen, insects,
bats and birds. |

This is a picture of NEXRAD radar station.
Back to top of page
What is radar?
 |
Radar is an acronym for radio detecting and
ranging system. |
 |
Radar uses the process of transmitting short
bursts or microwave energy in the direction of the object of interest. |
 |
The energy is scattered and some of the energy
comes back to be measured by the radar receiver. |
 |
Reflectivity is the term used to describe the
energy returned to the radar receiver. |
 |
Reflectivity is measured in decibels, dBZ. |
 |
Radar was originally used during World War II to
detect enemy aircraft. |
 |
Radar operators noted small blips on their
screens which they referred to as angels. |
 |
Radar today has many application such as weather
tracking, animal tracking, smog and pollen counts and wind direction. |
 |
Data from radar provides insights into migration
and important stop over sights. |
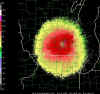
This is a radar image of heavy
migration of orioles the night of April 29-30, 2001 near Milwaukee,
Wisconsin. Note the
legend on the left hand side of the map showing reflectivity in decibels.
Back to
top of page
How does radar work?
 |
Microwave energy is emitted through an antenna of
a radar station. |
 |
Energy moves toward the object of interest. |
 |
When energy reaches the object the energy
scatters. |
 |
The bigger the object or group of objects the
stronger the scattered signal. |
 |
The radar then receives the returned signal
(reflectivity). |
 |
Data (images) can be viewed on a radar screen or
stored in a computer for further analysis. |
 |
Data is recorded 24/7. |
Back
to top of page
Using radar to detect
birds
 |
NEXRAD operates in two modes: Precipitation and
Clear Air. |
 |
When birds are the object of interest or target,
the Clear Air mode is used. |
 |
Clear Air mode has a longer dwell time and is
more sensitive to scattered energy, it picks up lower decibels. |
 |
Observations have shown that birds register in
the decibel (dBZ) range of 30-35 dBZ. |
 |
When using radar to detect birds there are other
factors to consider when analyzing the data: |
*Appearance of image on the radar screen
*Speed and direction of
image on the radar screen
*Reflectivity patterns on
the radar screen
*Wind measurements (birds
at times fly in a different direction of the wind)
 |
Radar is useful to track birds that fly at night
or at high altitudes. |
 |
Radar images can be used with bioacoustic
records, satellite thermal imagery, counting birds by sight and
identifying species by sight (ground truth). |
 |
The best time to monitor birds is at dusk. |
Back to
top of page
Limitations
 |
Researcher cannot tell which bird species are migrating from
image alone. |
 |
Bird migration can not be tracked during heavy
rainfall. |
 | Since birds migrate only twice per year,
researchers are limited to the time of year they can track migration. |
Back
to top of page
|