|
|
| One of the sensors among SPOT 4/5 is the
VEGETATION sensor and this gathers data, which is detailed
further in the Sensors page. VEGETATION data can be
used for various applications. Below is a list of
applications that the VEGETATION data gathered by the SPOT
satellite can be used for (SPOT
Vegetation). |
| |
| |
|
Agriculture: Crop monitoring, crop production, early
warning system to prevent food shortage, improve decision
support tools and optimize the actions of governments, and
help food aid agencies. |
| |
|
Water Resource Management: Water resource mapping and
monitoring for the optimization of irrigation management and
snow cover monitoring for flood prevention. |
| |
|
Forestry: Forest mapping and change detection. |
| |
|
Land Planning: Land cover map to be used for zoning
processes and the elaboration of resource mangement plans. |
| |
|
Environment: Disaster mapping and monitoring for
damages and emergency preparedness. |
| |
|
Terrestrial Ecosystems: Characterization of
terrestrial ecosystems and their seasonal dynamics. |
| |
|
Global Change: Change in vegetation through time. |
| |
|
Remote sensing is important because it helps to identify
most kinds of vegetative matter due to the vegetation, its
interactions with the soil, and its chemical nutrients
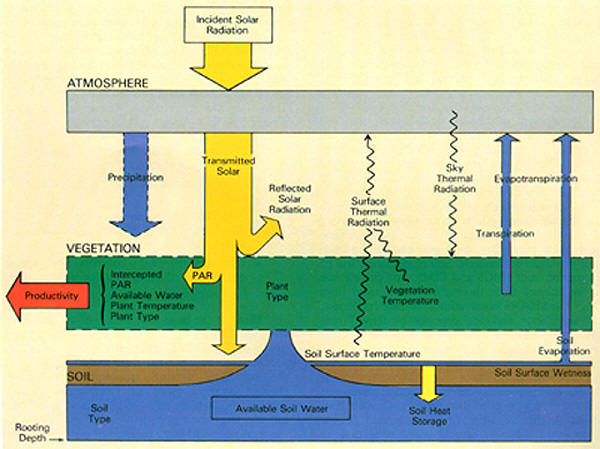
within. Below is a picture showing how various
conditions are involved in the productivity of the
vegetation (VEGETATION
Applications). |
 |
|
Image
from:
http://www.fas.org/irp/imint/docs/rst/Sect3/Sect3_1.html |
| |
|
Remote sensing is so useful due to the fact that it can
discriminate radiation absorption and reflectance of
vegetation. Leaves of most vegetation is slightly
transparent, which means the soil or whatever is beneath
will leave off some of its own signature as shown in this
picture. |
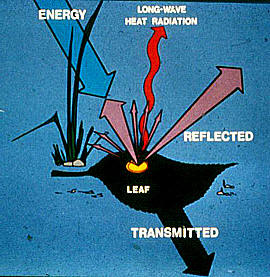 Image from
http://www.fas.org/irp/imint/docs/rst/Sect3/Sect3_1.html
Image from
http://www.fas.org/irp/imint/docs/rst/Sect3/Sect3_1.html |
| |
|
Remote sensing can help save farmers money and even increase
crop yield. If crops are being monitored farmers would
know ahead of time, which crops are going to be stressed due
to lack of moisture, or due to disease and pests. This
stress is shown in remote sensing when there is a
progressive decrease in Near-IR reflectance, but at the same
time an increase in Short-Wave IR reflectance as shown below
(VEGETATION
Applications). |
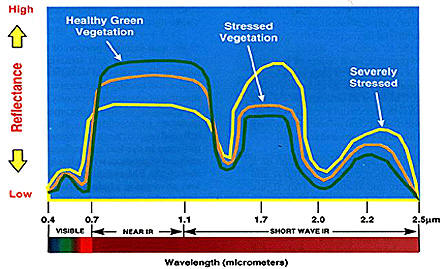
Image from
http://www.fas.org/irp/imint/docs/rst/Sect3/Sect3_1.html |
| |
|
As mentioned above stresses can be shown using remote
sensing. Above was spectral signatures showing the
stresses, but here is imagery showing the stress. In
this aerial photo the healthy vegetation is red, while the
stressed vegetation is more blue to yellow-white. |
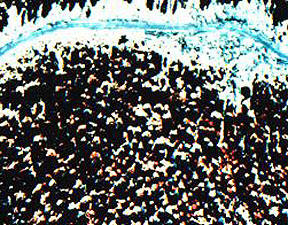
Image from
http://www.fas.org/irp/imint/docs/rst/Sect3/Sect3_1.html |
| |
|
Soil moisture plays an important part if crops will be
productive or not so knowing what crops need to be irrigated
can help the crops and also save water and money on not
irrigating crops that don't need it. Below is a
picture showing moisture content using thermal imagery.
Thermal imagery was used because for the most part soils
lacking water or ones that are stressed are generally
warmer. The lighter color soils are ones that could
use a good watering or two (VEGETATION
Applications). |
 Image from
http://www.fas.org/irp/imint/docs/rst/Sect3/Sect3_1.html
Image from
http://www.fas.org/irp/imint/docs/rst/Sect3/Sect3_1.html |
| |
| |