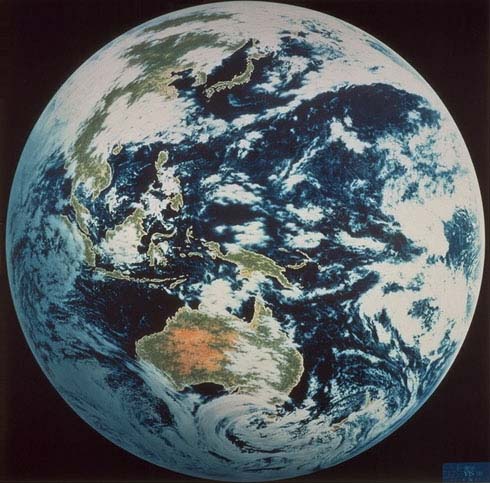

Earth Observation Satellites From Japan

Image transmitted from Himawari
This page introduces earth observation satellites owned by Japan.
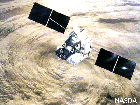 Tropical
Rainfall Measuring Mission [TRMM]
Tropical
Rainfall Measuring Mission [TRMM]
TRMM is the first space mission dedicated to quantitatively measuring tropical and subtropical rainfall which is one of the most important and least-known parameters affecting the global climate system. Operating : 1997-
 Geostationary
Meteorological Satellites: GMS [Himawari], GMS-2 [Himawari-2], GMS-3
[Himawari-3], GMS-4 [Himawari-4], GMS-5
Geostationary
Meteorological Satellites: GMS [Himawari], GMS-2 [Himawari-2], GMS-3
[Himawari-3], GMS-4 [Himawari-4], GMS-5
The Geostationary Meteorological Satellites (GMS) built by Hughes Space and Communications Company (HSC) for Japan have provided uninterrupted monitoring of weather conditions. Operating : 1977-
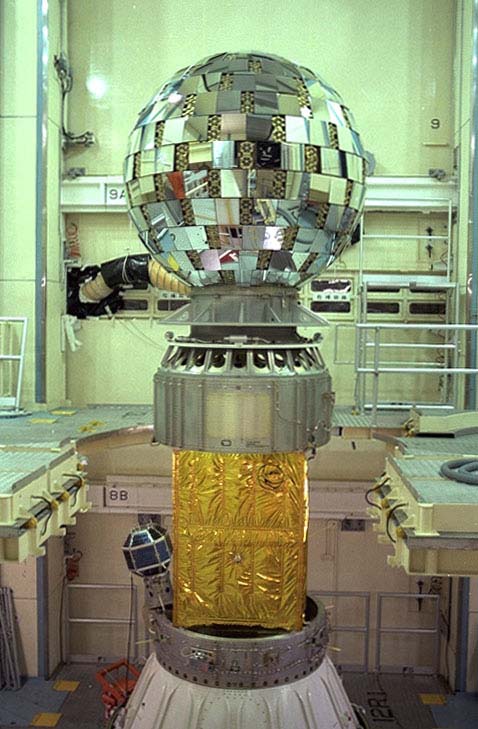 Experimental
Geodetic Satellite: EGS [Ajisai]
Experimental
Geodetic Satellite: EGS [Ajisai]
The primary short-range objective for EGS was testing of NASDA's H-I'(2-stage) launch vehicle. Long-range applications included a survery aimed at rectifying Japan's domestic geodetic triangular net - determining the exact position of many isolated Japanese islands and establishing Japan's geodetic point of origin. Operating : 1986-
 Advanced Land Observing Satellite
[ALOS]
Advanced Land Observing Satellite
[ALOS]
The Advanced Land Observing Satellite is the satellite that follows JERS-1 and ADEOS and enhance their land observing technology. ALOS will be used for cartography, regional observation, disaster monitoring, and resource surveying. Launch : 2003 (scheduled)
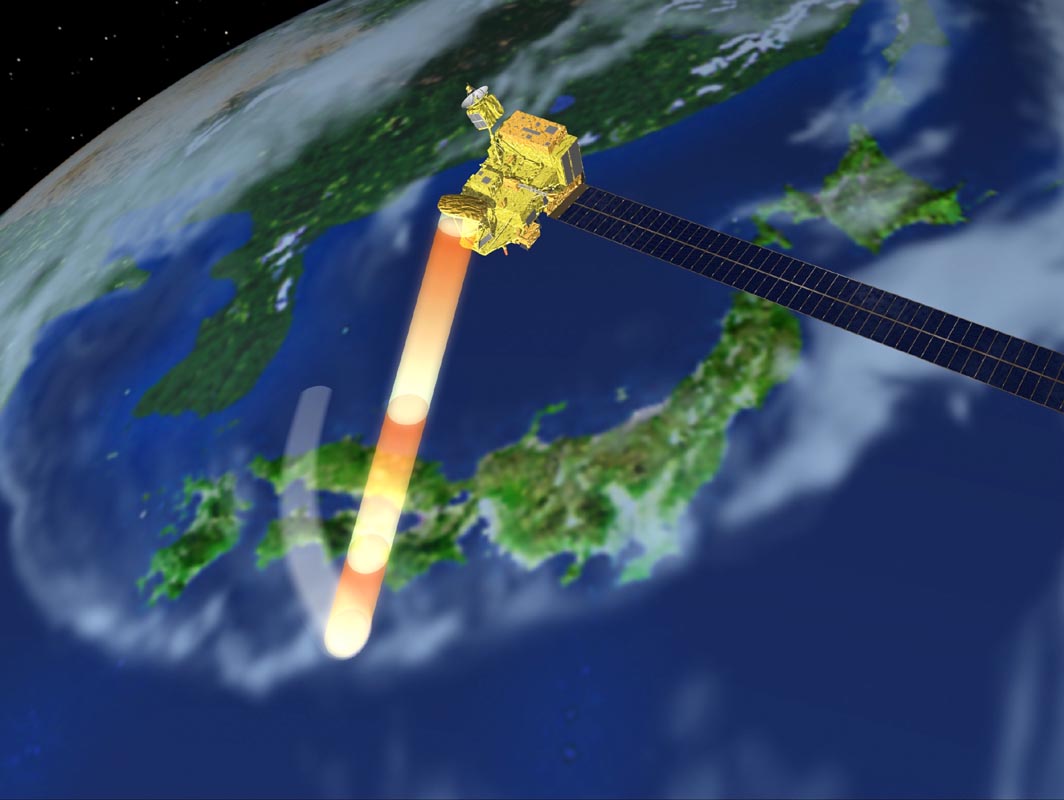 Advanced Earth Observation Satellite [ADEOS-II]
Advanced Earth Observation Satellite [ADEOS-II]
The Advanced Earth observing Satellite II(ADEOS-II) will be launched by H-IIA launch vehicle in 2002. ADEOS-II will take over ADEOS's observation mission of monitoring frequent climate changes occurring in the world, expansion of the ozone holes, and global environmental changes, as well as investigating the causes of these phenomena. Launch : 2002 (scheduled)
 Advanced
Earth Observing Satellite [ADEOS]
Advanced
Earth Observing Satellite [ADEOS]
ADEOS acquired the data on global warming, destruction of the ozone layer, decrease of tropical rain forests and climate changes. Operating end : 1996-1997
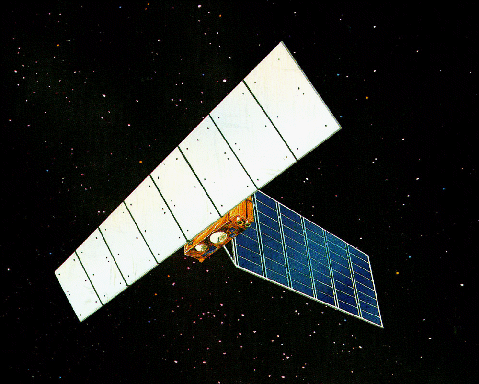 Japanese
Earth Resources Satellite: JERS-1 [Fuyo-1]
Japanese
Earth Resources Satellite: JERS-1 [Fuyo-1]
JERS-1 is an Earth Observation Satellite to cover the global land area for national land survey, agriculture, forestry, fishery, environmental preservation, disaster protection and coastal monitoring, etc. focusing on natural resource exploration. Operating end : 1992-1998
 Marine
Observation Satellite: MOS-1 / MOS-1b [Momo-1/Momo-1b]
Marine
Observation Satellite: MOS-1 / MOS-1b [Momo-1/Momo-1b]
Marine Observation Satellite is the Japan's first Earth Observation Satellite developed applying domestic technologies as a part of Satellite Earth Observation Systems for contributing to effective utilization of Earth resources, environmental protection and so on. Operating end : 1987-1996
 Ionosphere
Sounding Satellites: ISS [Ume] and ISS-b [Ume-2]
Ionosphere
Sounding Satellites: ISS [Ume] and ISS-b [Ume-2]
The satellites were intended for regular observation of global distribution of critical frequencies of the ionosphere, and for utilization of the results of the observation for radio wave forecasts and warning necessary for effective operation of short-wave radio-communication. Operating end : 1976-1983
The Texas Grant Consortium Mission characterizations of different space satellites
Topographic Engineering Center Characteristics of remote sensing systems and basic sensor information
The Visual Science Center Principles of remote sensing
Popular Science 5 Year Guide to Space Exploration Characteristics of future satellite mission
Federation of American Scientists Information of Japanese Space activities
Images and information used on this page are from the following web sites :
National Aeronautics and Space Administration [NASA]
National Space Development Agency of Japan [NASDA]
International Laser Ranging Service
Remote Sensing Technology of Japan [RESTEC]
Web Page Created by:
Rie Matsubayashi
Department of Geography
Salem State College, Salem, MA USA